Apache SSL Termination (HTTPS Varnish cache)
I have seen several posts on how to configure SSL offloading using Nginx, but I was unable to find complete instructions for Apache. It also so happened, that I prefer Apache web server over Nginx. That fact made me create this short post.
In this post, I’d like to describe the SSL termination approach in general and provide the specific configuration for the Apache2 web server.
General approach
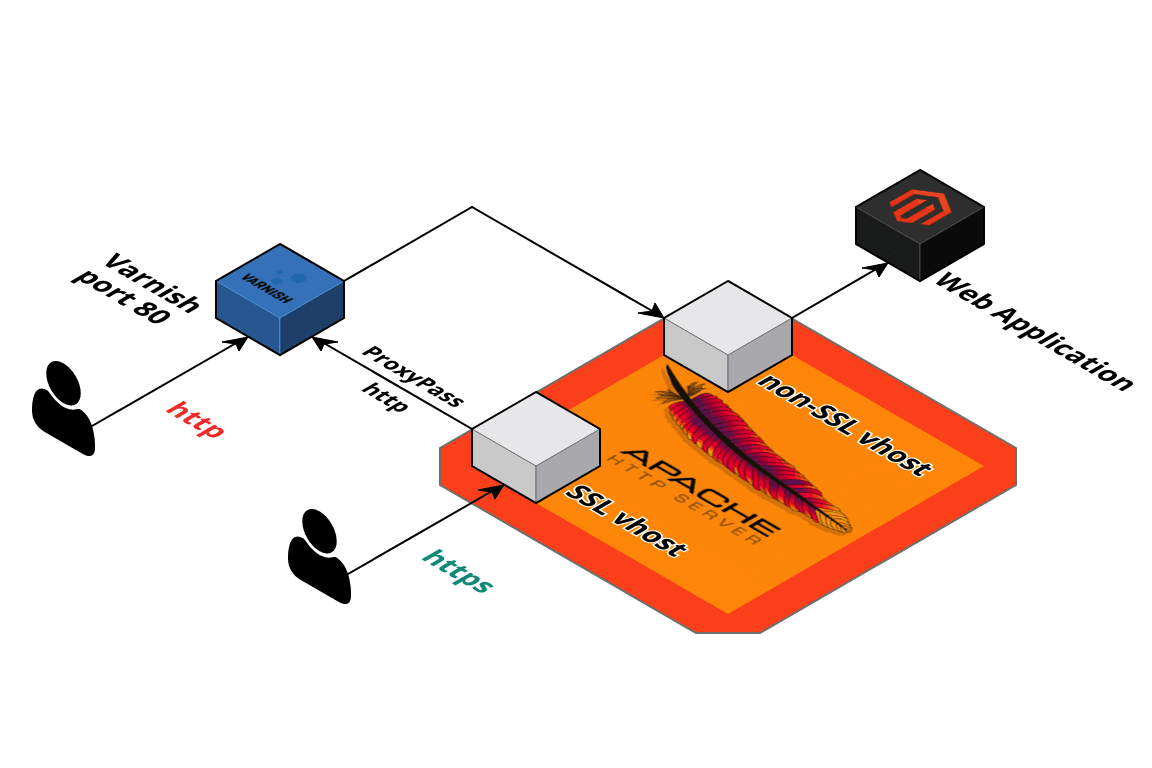
The idea is to set up an environment with:
- Varnish with frontend on port 80 and backend on port 8080
- The first website that listens to port 8080 and serves the web application (Magento 2 in this example)
- Second web site listening to port 443, handling SSL and proxy passing traffic to Varnish on port 80
The following instructions are based on Ubuntu 16 and Apache 2.4.
Varnish configuration
Varnish configuration does not make too much difference here, for consistency with other components it’s important to ensure that Varnish frontend and backend are on correct ports:
An important part for VCL file (/etc/varnish/default.vcl)
...
backend default {
.host = "127.0.0.1";
.port = "8080";
}
...
Port 80 is expected to be used for frontend in /etc/systemd/system/varnish.service file (or /etc/default/varnish on older Linux)
Apache configuration
There are two virtual hosts that should be configured on the Apache side.
The first virtual host is the basic one that is server web application on port 8080.
ServerName localhost.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/magento/pub
Make sure apache is listening to port 8080 (/etc/apache2/ports.conf).
The second virtual host is a bit more complicated as it utilizes extra apache 2 modules, handles SSL and proxies the request.
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto "https"
ServerName localhost.com
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile /etc/apache2/ssl/cert.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/apache2/ssl/cert.key
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyPass / http://127.0.0.1:80/
ProxyPassReverse / http://127.0.0.1:80/
The “X-Forwarded-Proto” header is not required for the setup to work, however, it is quite useful and may be necessary for correct work of web frameworks. It’s also known as “offloading” header.
Apache modules
As you might already notice from the virtual host configuration file that there are several mods that have to be enabled.
sudo a2enmod ssl
sudo a2enmod rewrite
sudo a2enmod headers
sudo a2enmod proxy
sudo a2enmod proxy_balancer
sudo a2enmod proxy_http
Finally, don’t forget to enable virtual hosts and restart the web server.
sudo service apache2 restart

